Reservation Communities Install New Membrane Systems
By Michael Bourke and Susan Guibert
The Fort Berthold Indian Reservation is located in the heart of the oil boom region in North Dakota. This boom has driven the demand for improved infrastructure in this isolated region, including water treatment facilities.
The reservation's existing water treatment plants, consisting of packaged coagulation/sedimentation/gravity filtration systems, were nearing the end of their useful life with turbidity breakthrough incidents becoming more frequent.
Engineering consultant Bartlett and West was engaged to conduct a review of upgrade options for the reservation's treatment plants and selected ACH coagulation/plate settlers followed by ultrafiltration as the most suitable alternative.
Wigen Water Technologies was subsequently awarded a contract in 2010 to install UF systems for the communities of Newtown, Mandaree and Twin Buttes. The Four Bears WTP at Newtown, consisting of two 700 gpm skids, was the first to start up in May 2011. The Mandaree WTP consisting of two 500 gpm skids was started up in July 2011.
The two systems are using Toray's HFS-2020 UF membrane modules. The reservation's third system at Twin Buttes is yet to be installed but will also use the membrane modules. Each of these systems source water from Lake Sakakawea which is located on the upper reaches of the Missouri River.
These systems are the first large scale opportunity in North America to review the performance of the Toray UF membranes in terms of integrity, flux rates and fouling characteristics.
The company's HFS-2020 module is a pressurized outside-in module with hollow fiber PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) membranes having a nominal pore diameter of 0.02 µm. The membrane surface area in each module is 775 ft2. These membranes are manufactured using the Thermally Induced Phase Separation (TIPS) process which is believed to produce a membrane that is much less susceptible to breakages compared to other hollow-fiber membranes.
The membrane fibers have an outside diameter of 1.5 mm and a wall thickness of 0.3 mm. Wall thickness also has been determined to be an important factor in minimizing fiber breakages. Fewer fiber breakages have been encountered at installations using PVDF membranes with greater fiber thicknesses [Stratton and Chang, 2011]. The Toray UF membrane fiber has one of the thickest walls of the commercially available PVDF membranes.
The HFS-2020 module was approved by the Californian Department of Public Health (CDPH) for at least 4-log Giardia and Cryptosporidium removal and a maximum flux of 120 gfd in September 2007. While it is unlikely that a drinking water UF system would be designed for such high flux rates, the high flux rates and higher module membrane surface area can result in a smaller UF system footprint and reduced capital costs.
Design Information
Both the Four Bears and Mandaree installations consist of two UF skids with 100% redundancy so that the full capacity can be provided with one skid out of service. Raw water is first dosed with Aluminum Chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to a MRI plate settler. Settled water from the plate settler flows by gravity to a feed water tank dedicated to each UF skid from where feed pumps on the UF skids deliver this water through prescreens and then to the UF modules. The feed pumps operate based on level controls in the feed water tanks.
Wigen Water Technologies' scope of supply for these projects was as follows:
- 2 UF skids, including feed pumps, prescreens and backwash water holding tank.
- Feed water tanks and instrumentation for feed pump control.
- Backwash holding tank and backwash pump skid with associated controls and panel.
- CIP tank and CIP pump/filter skid and control system.
- Dedicated PLC control system on each UF skid.
UF System Performance
At start-up of both UF systems, no fiber breakages or leaks were detected and pressure decay test results correlated with greater than 4-log removal of Giardia and Cryptosporidium. No fiber repairs were necessary in the first year of operation. Daily pressure decay tests (PDTs) have resulted in a Log Removal Value (LRV) of greater than 4.0 since start-up. This calculation is based on the Darcy pipe flow model which is the more conservative method for calculating the log removal credit. The average pressure drop over the five minute PDT was 0.04 psi/min.
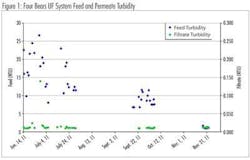
The feed and permeate turbidity levels since start-up of the Four Bears WTP are shown in Figure 1. High rainfall in the region around the time of plant startup resulted in very high raw water turbidities and even after coagulation and plate setting the settled water feed to the UF system was often over 20 NTU.
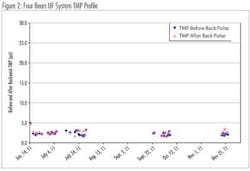
While the design CIP frequency for the UF system at the Four Bears WTP was every three months, the first CIP was not conducted until around six months after start-up. With a daily chemically enhanced backwash (CEB) using a chlorine dose of 300 mg/L, Figure 2 shows there was virtually no increase in UF system TMP between CIP intervals.