Testing Optimizes Activated Carbon for TTHM Removal
By Kimberly Thompson
Chlorination of drinking water has all but eliminated waterborne diseases such as typhoid fever, cholera and dysentery. Proper chlorination kills the bacteria, viruses and parasites responsible for these illnesses.
Unfortunately, there are several byproducts from the chlorination of drinking water that pose a possible health risk. Some of these byproducts include trihalomethanes (THMs), bromate, chlorite and the five newly regulated haloacetic acids (HAA5's).
Chloroform, bromoform, dibromochloromethane, and dichlorobromomethane collectively make up what are known as total trihalomethanes (TTHMs), which are created when the disinfectant (chlorine) used in water treatment reacts with bromide or natural organic matter (decaying vegetation) present in the source water.
TTHM Regulation
Regulation of TTHMs in drinking water supplies dates to 1979, when the EPA introduced the Total Trihalomethane Rule. More recently, the Stage 1 Disinfection Byproduct Rule (DBPR) was promulgated in 1998 to monitor and reduce disinfection byproducts.
The EPA is now working on the next phase of legislation, Stage 2 DBPR, related to disinfection byproduct control, and a draft was issued in October 2001. The emphasis of Stage 2 is to reduce peak DBP levels by changing monitoring locations within water systems, and by measuring for TTHMs and HAA5s using a locational running annual average (LRAA) at each sample point (Stage 1 required a system-wide running annual average). Water systems impacted by the rule will have to meet the MCL for TTHMs and HAA5s at each sample point.
Initial compliance to Stage 2 will require meeting a 0.12 mg/L MCL for TTHMs and 0.10 mg/L MCL for HAA5s as a LRAA at each current sample point used for Stage 1 monitoring. Within three to seven years, depending on system size, compliance with the MCL of 0.080 mg/L for TTHMs and 0.060 mg/L for HAA5s will be required as a LRAA at each new Stage 2 monitoring point within the water system.
The EPA is currently seeking comments on the proposed rule, and a final rule is expected late in 2002 or in 2003. While full compliance requirements are several years away, this rule will continue to increase the awareness of THM issues and proper THM control in water systems.
Dealing with TTHMs
There are many options, including reduction of chlorine use at the treatment plant and switching to alternative methods of disinfection, such as chloramines, ozone or ultraviolet (UV), for the reduction of TTHMs. The proposed Stage 2 DBPR lists granular activated carbon along with nanofiltration as a best available technology (BAT) for TTHM removal. The following discussion highlights the carbon characteristics that are desired to optimize the carbon's performance for TTHM removal.
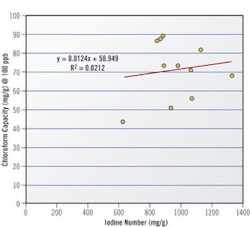
Selection of the correct activated carbon is key to the success of applying activated carbon to any application, including TTHMs. Historically, the parameter used when selecting a carbon is Iodine Number, which was developed because iodine is safe to handle, is well adsorbed onto activated carbon, and the test is easy to run with repeatable results. However, iodine number is not very effective at gauging a carbon's performance at adsorbing trace levels of contaminants. For example, no correlation exists between Iodine Number and chloroform capacity for a representative sampling of numerous activated carbons.
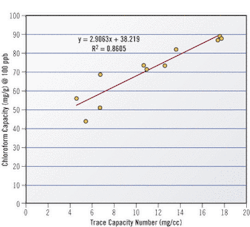
Given the limitations of Iodine Number in trace removal applications, carbon manufacturers are beginning to use new measures to better characterize an activated carbon's trace capacity. One new measure, called the Trace Capacity Number, measures a carbon's capacity to adsorb acetoxime, a more realistic surrogate for low-level contaminant concentrations than iodine. Comparing trace capacity number with chloroform capacity yields a much better correlation than iodine number.
Column Testing
To demonstrate the comparison of Iodine Number and Trace Capacity Number with respect to TTHM removal, two activated carbons were selected and tested side by side in a 1 inch column study. Unlike adsorption isotherms, which are commonly used to characterize activated carbons, column studies obtain breakthrough curves under dynamic conditions, and show how the concentration of the contaminants in the effluent will vary with the volume of liquid treated.
Furthermore, the rate at which the contaminants are adsorbed by the carbon can only be determined by dynamic column tests. Understanding these kinetics of adsorption allows for proper system design.
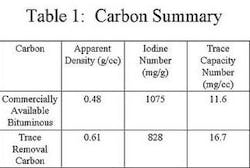
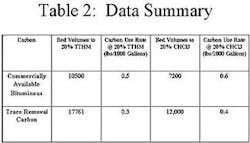
The first activated carbon selected in this study was a commercially available bituminous coal-based carbon that had not been optimized for trace capacity. The second carbon selected, also commercially available, was optimized for Trace Capacity Number. Both carbons had similar Iodine Numbers, but varied with regard to Trace Capacity Number. The water used in the column study was tap water containing influent levels of chloroform that averaged 12 ppb, and TTHM levels that averaged 75 ppb.
In this study, the activated carbon optimized for trace removal outperformed the standard bituminous carbon in the dynamic test. Clearly, the carbon with a higher Trace Capacity Number yields improved performance for TTHM removal. Improved performance translates to less frequent carbon exchanges, easier system operation, and most importantly, lower operating costs for the customer.
Other water characteristics that can impact the life of the activated carbon must also be taken into account when applying carbon for TTHM removal. Background organics (often measured as Total Organic Carbon, or TOC) can competitively adsorb and shorten the bed life of the carbon, and inorganics such as iron can precipitate onto carbon beds and impact carbon performance. Proper monitoring and backwashing of carbon beds is recommended to ensure that the carbon is working properly and that the system is maintained.
While chlorination of drinking water has its benefits, it also has its drawbacks through the formation of TTHMs. Fortunately, water treatment professionals have tools at their disposal to deal with TTHM problems in their water supply. Activated carbon, when properly selected and applied, is one of those tools.
About the Author
Kimberly Thompson is a research and development chemist at Calgon Carbon Corp. in Pittsburgh, PA.