MIT scientists develop method for simple, solar-powered water desalination
MASSACHUSETS, FEB 18, 2020 -- A completely passive solar-powered desalination system developed by researchers at MIT and in China could provide more than 1.5 gallons of fresh drinking water per hour for every square meter of solar collecting area. Such systems could potentially serve off-grid arid coastal areas to provide an efficient, low-cost water source.
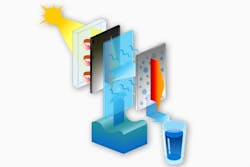
The system uses multiple layers of flat solar evaporators and condensers, lined up in a vertical array and topped with transparent aerogel insulation. It is described in a paper in the journal Energy and Environmental Science, authored by MIT doctoral students Lenan Zhang and Lin Zhao, postdoc Zhenyuan Xu, professor of mechanical engineering and department head Evelyn Wang, and eight others at MIT and at Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China.
The key to the system’s efficiency lies in the way it uses each of the multiple stages to desalinate the water. At each stage, heat released by the previous stage is harnessed instead of wasted. In this way, the team’s demonstration device can achieve an overall efficiency of 385 percent in converting the energy of sunlight into the energy of water evaporation.
The device is essentially a multilayer solar still, with a set of evaporating and condensing components like those used to distill liquor. It uses flat panels to absorb heat and then transfer that heat to a layer of water so that it begins to evaporate. The vapor then condenses on the next panel. That water gets collected, while the heat from the vapor condensation gets passed to the next layer.
Whenever vapor condenses on a surface, it releases heat; in typical condenser systems, that heat is simply lost to the environment. But in this multilayer evaporator the released heat flows to the next evaporating layer, recycling the solar heat and boosting the overall efficiency.
“When you condense water, you release energy as heat,” Wang says. “If you have more than one stage, you can take advantage of that heat.”
Adding more layers increases the conversion efficiency for producing potable water, but each layer also adds cost and bulk to the system. The team settled on a 10-stage system for their proof-of-concept device, which was tested on an MIT building rooftop. The system delivered pure water that exceeded city drinking water standards, at a rate of 5.78 liters per square meter (about 1.52 gallons per 11 square feet) of solar collecting area. This is more than two times as much as the record amount previously produced by any such passive solar-powered desalination system, Wang says.
Unlike some desalination systems, there is no accumulation of salt or concentrated brines to be disposed of. In a free-floating configuration, any salt that accumulates during the day would simply be carried back out at night through the wicking material and back into the seawater, according to the researchers.
Their demonstration unit was built mostly from inexpensive, readily available materials such as a commercial black solar absorber and paper towels for a capillary wick to carry the water into contact with the solar absorber. In most other attempts to make passive solar desalination systems, the solar absorber material and the wicking material have been a single component, which requires specialized and expensive materials, Wang says. “We’ve been able to decouple these two.”
The most expensive component of the prototype is a layer of transparent aerogel used as an insulator at the top of the stack, but the team suggests other less expensive insulators could be used as an alternative. (The aerogel itself is made from dirt-cheap silica but requires specialized drying equipment for its manufacture.)
Wang emphasizes that the team’s key contribution is a framework for understanding how to optimize such multistage passive systems, which they call thermally localized multistage desalination. The formulas they developed could likely be applied to a variety of materials and device architectures, allowing for further optimization of systems based on different scales of operation or local conditions and materials.
One possible configuration would be floating panels on a body of saltwater such as an impoundment pond. These could constantly and passively deliver fresh water through pipes to the shore, as long as the sun shines each day. Other systems could be designed to serve a single household, perhaps using a flat panel on a large shallow tank of seawater that is pumped or carried in. The team estimates that a system with a roughly 1-square-meter solar collecting area could meet the daily drinking water needs of one person. In production, they think a system built to serve the needs of a family might be built for around $100.
The researchers plan further experiments to continue to optimize the choice of materials and configurations, and to test the durability of the system under realistic conditions. They also will work on translating the design of their lab-scale device into a something that would be suitable for use by consumers. The hope is that it could ultimately play a role in alleviating water scarcity in parts of the developing world where reliable electricity is scarce but seawater and sunlight are abundant.
“This new approach is very significant,” says Ravi Prasher, an associate lab director at
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and adjunct professor of mechanical engineering at the University of California at Berkeley, who was not involved in this work. “One of the challenges in solar still-based desalination has been low efficiency due to the loss of significant energy in condensation. By efficiently harvesting the condensation energy, the overall solar to vapor efficiency is dramatically improved. … This increased efficiency will have an overall impact on reducing the cost of produced water.”
The research team included Bangjun Li, Chenxi Wang and Ruzhu Wang at the Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Bikram Bhatia, Kyle Wilke, Youngsup Song, Omar Labban, and John Lienhard, who is the Abdul Latif Jameel Professor of Water at MIT. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology, and the MIT Tata Center for Technology and Design.