Digital transformation drives maintenance excellence at Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District
When managing hundreds of control valves across a sprawling water distribution system, accurate data and efficient maintenance scheduling can mean the difference between smooth operations and potential system failures. For Elsinore Valley Municipal Water District (EVMWD), serving 163,000 customers across 97 square miles in California, the challenge of maintaining 385 valves at 150 sites demands a sophisticated solution to enhance accuracy, streamline maintenance scheduling, and improve asset management.
The district's infrastructure includes 14 active wells, 70 active storage reservoirs, 55 booster pumping stations, and 44 pressure reducing stations, all connected by 743 miles of pipeline. Managing this complex network spanning from flat city terrain to mountainous rural areas efficiently requires precise coordination and accurate data — a challenge that EVMWD has tackled head-on through digital transformation.
The journey began serendipitously when operators discovered a QR code on a new Cla-Val pressure reducing valve. This discovery led to the implementation of Link2Valves, a data management platform specifically designed for water utilities. Water District Supervisor Brian Vigil recognized the potential immediately, saying "We were keen to improve our valve maintenance schedule and the first step in this process is knowing everything we can about each valve in our system. Then we have a much better picture on which stations need maintenance or budget planning for replacement."
Building a powerful data bank
One of the primary challenges facing EVMWD was maintaining accurate, up-to-date information about their valve infrastructure. "The information for each control valve was not up to date and therefore inaccurate in our GIS database," explains Vigil. "As operators, we would have to work closely with our GIS staff to update each valve, which can be a long process, and some information can get lost in translation."
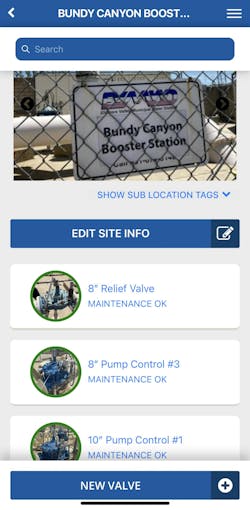
The implementation process began with hands-on support from their Cla-Val representative, who helped input nearly every valve in the water distribution system into the platform, along with information on installation dates, sizes, functions. "This was extremely helpful in getting us started," notes Vigil. The team has since been systematically adding specific pilotry and set points on relief valves and reducing valves during their quarterly site visits.
The new program has streamlined the district’s approach to data management. The platform allows operators to collect and store accurate information directly from the field, including photographs, valve locations, settings, and complete service histories. This real-time data collection has significantly improved the accuracy of their asset information and eliminated the communication gaps that previously existed between field operators and GIS staff.
Streamlining maintenance scheduling
The district has implemented a sophisticated maintenance scheduling system based on 2.5-year and 5-year maintenance intervals. The platform's interface features a color-coded pie chart that quickly identifies maintenance priorities.
For Jordan Velasco, district water operator for EVMWD, this tool has made a particular impact on daily operations. "My favorite feature is the pie chart that shows what stations are red and need immediate attention, to yellow which are the upcoming sites that will need attention soon, to green which shows sites that have already been serviced," he shares. This visual approach makes it easy to plan and respond to issues, keeping Velasco’s team one step ahead.
The system also serves as a knowledge management tool, which is useful for new hires or employees that are unfamiliar with every site. It provides exact location information and specific set points for pressure reducing valves, relief valve settings at the pump stations, and reservoir set points on altitude valves. Additionally, having serial numbers readily available helps Velasco when it comes to ordering parts and ensuring that the team has what they need when they do their maintenance rounds.
Enhanced asset management and future planning
The platform is also being used for asset management and future planning. Operators can now track how long valves have been in the system and monitor their condition over time. The ability to store photos of control valves is a good visual data point for condition assessment and replacement planning.
"Having the ability to store photos of the condition of the control valves allows us to accurately produce condition assessment scores and budget for replacement costs," notes Vigil. This visual documentation, combined with detailed maintenance records, enables the district to develop more accurate lifecycle forecasts and implement robust predictive maintenance strategies.
Looking ahead, EVMWD is working with Cla-Val to integrate the platform's data into their GIS database, further enhancing their asset management capabilities. The district plans to use this integrated data to produce more sophisticated condition assessment scores and continue to streamline its maintenance and replacement schedules.
As Vigil reflects on their journey, he emphasizes the practical benefits, saying "Having access to an app which we can accurately record and store our information from the field is very beneficial."
While the platform itself is provided at no cost to users, EVMWD's investment in time and effort has already shown positive returns through improved asset management. The district anticipates even greater benefits as they continue to develop their predictive maintenance and replacement planning capabilities.
For water utilities facing similar challenges in managing complex valve infrastructure, EVMWD's experience demonstrates how embracing smart solutions, utilities can move from reactive maintenance to proactive asset management, ensuring more reliable service for their customers while optimizing operational resources.
About the Author
Tina Christie
Tina Christie is the area sales manager for Cla-Val.