Back To Basics: Pump Specific Speed and Suction Specific Speed
By Allan R. Budris
My columns to date have generally assumed a knowledge of basic pump terminology by the readers. However, I am beginning to realize that not every pump user possesses this rudimentary understanding of pumps. This column describes two very basic, similar and useful centrifugal pump hydraulic characteristics. They are “Specific Speed” and “Suction Specific Speed”. While Specific Speed refers to the discharge characteristics of a pump, Suction Specific Speed, as the name implies, refers to the suction characteristics. In should be noted that the values of both of these terms remain constant for a given pump, regardless of the speed of the pump.
null
Specific Speed
The Specific Speed of a pump is defined by the following equation, in US units:
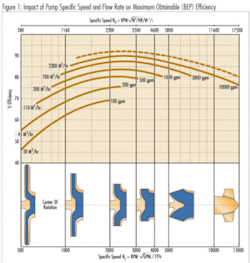
According to the definition for Specific Speed, pumps that develop a high flow and low head have relatively high specific speed values, while pumps that develop high heads at low flow rates have low specific speeds. Specific speed values range from a low of 500 to a high of about 10,000, with the more typical range being between 1,000 and 5,000.
Knowing the Specific Speed of a pump is useful in several ways:
It dictates the basic geometry of the impeller, with low Specific Speed pumps having large outside diameters and narrow, radial flow passages and high Specific Speed pumps having small outside diameters and large, more axial flow passages. Pumps of the same Specific Speed can be scaled up or down for greater or less flow and head requirements.
It dictates the shape of the head-capacity curve, with low Specific Speed pumps having flat or drooping H-Q curves, and high Specific Speed pumps having very steep curves. The pump shut-off flow brake horse power also increases with increasing Specific Speed values, exceeding the best efficiency flow input power requirements at “NS” values above about 4,500 to 5,000.
It dictates the maximum obtainable efficiency, as shown in figure 1, with the maximum obtainable efficiencies occurring at Specific Speed values between about 2,000 and 3,000. This is where multistage pumps come in. If the application calls for a low single stage Specific Speed value of 500 – 1200 or lower, then by adding additional impeller stages, which reduces the head produced by each stage, the Specific Speed value of the pump is increased. This then results in an increase in the efficiency of the pump. This is one of the advantages of vertical turbine pumps, which can change the number of impeller stages with little effort.
Specific Speed, coupled with the pump discharge head, helps determine the “Discharge Energy” level of a centrifugal pump. According to the Hydraulic Institute, below a Specific Speed value of 1,300, “High Discharge Energy” starts at a total developed head (TDH) of 900 feet, and this gating head value decreases as the Specific Speed values increase, to a low of 200 feet, at a Specific Speed of 2,700. High Discharge Energy pumps are more susceptible to discharge pressure pulsation problems from close impeller to volute tongue clearances, and poor discharge piping.
As spelled out in the April 2009 Column, pumps with Specific Speed values above 3,500 require greater (2 times) the minimum straight suction pipe lengths, to avoid suction related problems.
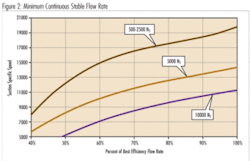
As shown in figure 2, Suction Recirculation starts at higher flow rates for pumps with Specific Speed values above 2,500, for the same Suction Specific Speed. High Suction Energy pumps (October 2007 Pump Tips Column) operated in the Suction Recirculation flow region are likely to experience cavitation damage.
Suction Specific Speed
The Suction Specific Speed of a pump is defined by the following equation, in US units:
Suction specific speed is an index number for a centrifugal pump similar to discharge specific speed and is used to define its suction characteristic. It is constant for a given pump, regardless of pump speed. Higher numerical values of “S” are associated with better suction capabilities. The numerical value of “S” is mainly a function of the impeller inlet and suction inlet design. For pumps of normal design, values of “S” vary from 6,000 to 12,000. In special designs, including inducers, higher values can be obtained, however, special materials may be required for continuous operation.
In the past, Suction Specific Speed alone was felt to predict pump reliability, with values above 11,000 felt to increase pump wear and failures. Based on these initial findings, many pump user company specifications limit pump selection to “S” values below 11,000. This approach has, however, since been found to be an over-simplification. The velocity of the impeller vane inlet tips, pump type and liquid specific gravity should also be considered in order to properly determine the potential reliability of a centrifugal pump. All of these factors are included in the authors “Suction Energy” concept (see October 2007 Pump Tips Column).
Knowing the Suction Specific Speed of a pump is useful in several ways:
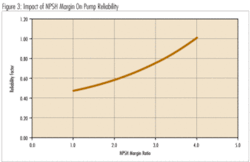
It shows how aggressive the pump impeller inlet design is (how low is the NPSHR for a given pump speed and BEP flow rate). Higher “S” values mean lower NPSHR and, therefore, greater NPSH Margins, which by itself, is a good thing (if it doesn’t push the pump into “High”, or “Very High” Suction Energy), see figure 3.
It is a key factor in calculating the “Suction Energy” (and therefore reliability) of a pump application.
Suction Specific Speed, coupled with “Suction Energy”, can be used to determine the maximum pump speed for an application to avoid excessive and damaging cavitation. Ideally pumps should be operated with low “Suction Energy”, and an NPSH Margin Ratio of at least 1.3, both of which can be achieved with slower pump speeds.
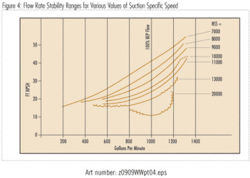
As mentioned above, Suction Specific Speed is another factor (in addition to Specific Speed) in determining the flow rate at which suction recirculation starts in a pump (see figure 2). Pumps with higher values of Suction Specific Speed typically have narrower “Allowable Operating Flow Regions”, see figure 4.
Based on the above, we can conclude that there are definite benefits from knowing the Specific Speed and Suction Specific Speed (plus Suction Energy) values for a pump, especially when comparing pump offerings for a specific proposal, and/or when generating a pump specification. WW
About the Author:
Allan R. Budris, P.E., is an independent consulting engineer who specializes in training, failure analysis, troubleshooting, reliability, efficiency audits and litigation support on pumps and pumping systems. With offices in Washington, NJ, he can be contacted via e-mail at [email protected].